The main types of Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) machines include rotary-type, linear-type, and shuttle-type. Rotary machines offer high-speed filling ideal for mass production. Linear machines allow for flexible configurations and are suitable for medium output. Shuttle-type machines are compact and ideal for low-volume or specialized applications.
Shuttle-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines
Shuttle-type BFS machines move plastic molds back and forth in a straight line to form containers. They’re the most common type of BFS machine in the industry.
These machines work well for making small to medium batches of products. Many companies choose shuttle-type machines because they’re flexible and can make different container shapes easily.
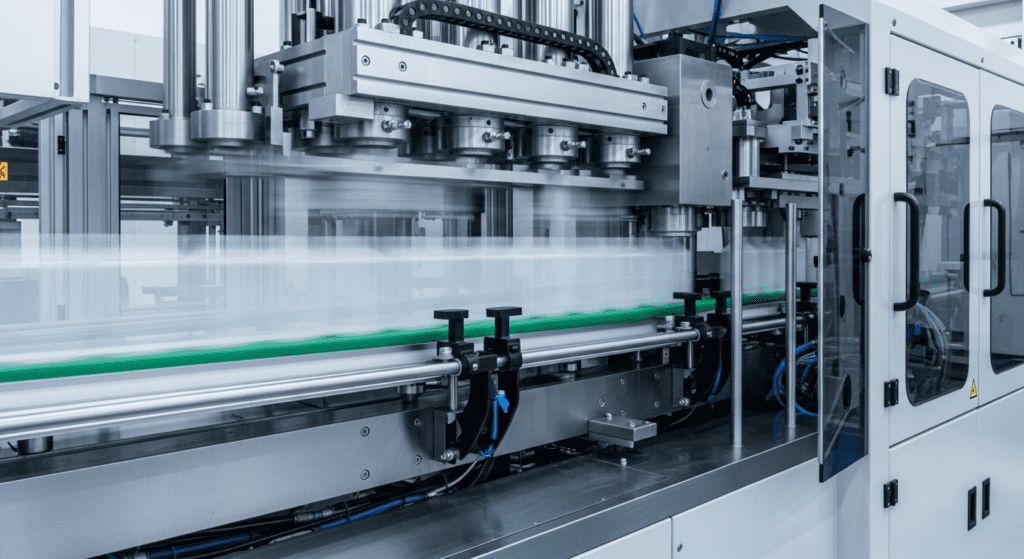
How Shuttle-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines Work
The shuttle-type machine starts by melting plastic resin into a soft tube called a parison. The machine then moves this hot plastic tube into a mold that shuttles horizontally.
Once the parison is in place, the mold closes around it. Sterile air blows into the plastic to form the container shape.
Next, filling nozzles come down and put the product into the newly formed container. The machine then seals the top while everything is still sterile.
Finally, the mold opens and shuttles back to its starting position. The finished containers drop out, and the whole process starts again.
Features of Shuttle-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines
- Quick changeover times – You can switch between different container sizes in 2-4 hours
- Container variety – Makes bottles from 0.1ml to 1000ml in size
- Production speed – Produces 3,000 to 15,000 units per hour depending on size
- Compact design – Takes up less floor space than rotary machines
- Easy maintenance – Fewer moving parts mean less things can break
- Lower initial cost – Costs 30-40% less than rotary-type machines
- Flexible operation – Can run different products on the same day
Rotary-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines
Rotary-type BFS machines use a spinning carousel design to make containers continuously. They’re perfect for high-volume production lines.
These machines never stop moving during production. The rotating design means they can make more containers per hour than other BFS types.
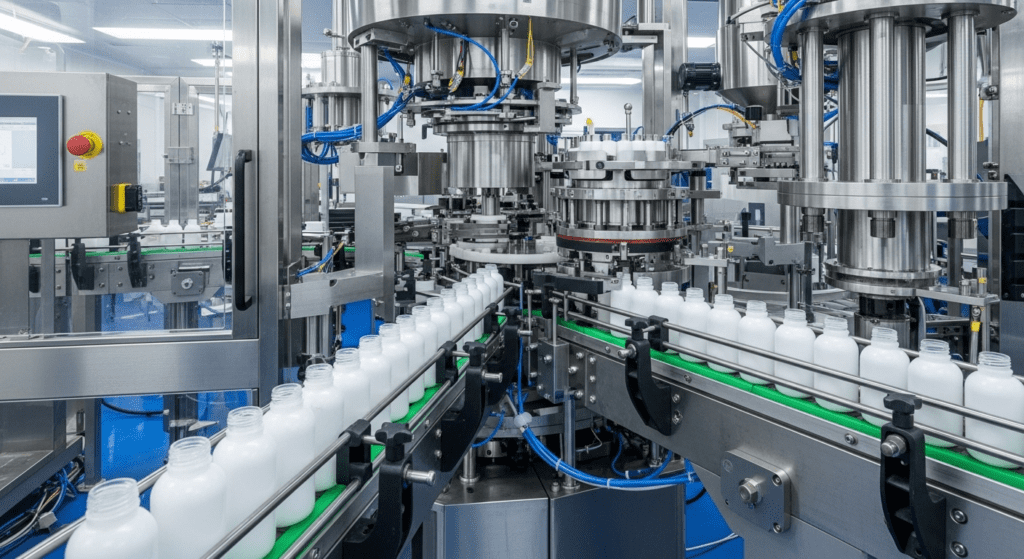
How Rotary-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines Work
A rotary BFS machine has multiple mold stations arranged in a circle. The plastic parison feeds continuously into these rotating molds.
As the carousel spins, each station goes through different steps. First, the mold closes around the hot plastic and blows it into shape.
The formed container keeps rotating to the filling station. Here, precise nozzles add the exact amount of product needed.
While still spinning, the container moves to the sealing station. The machine heat-seals the top before the mold opens.
The finished containers exit as the mold reaches its starting point. This continuous motion means there’s no stopping between cycles.
Features of Rotary-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines
- High-speed production – Makes 15,000 to 50,000 units per hour
- Continuous operation – Runs 24/7 with minimal downtime
- Multiple stations – Has 6-20 mold stations working at once
- Consistent quality – Produces very uniform containers
- Advanced automation – Uses robotics for inspection and packaging
- Energy efficient – Uses 20% less energy per unit than shuttle types
- Large batches – Ideal for products that need millions of units yearly
Linear-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines
Linear-type BFS machines move containers in a straight line through different stations. They combine features from both shuttle and rotary designs.
These machines work best for specialty products or when you need extra processing steps.
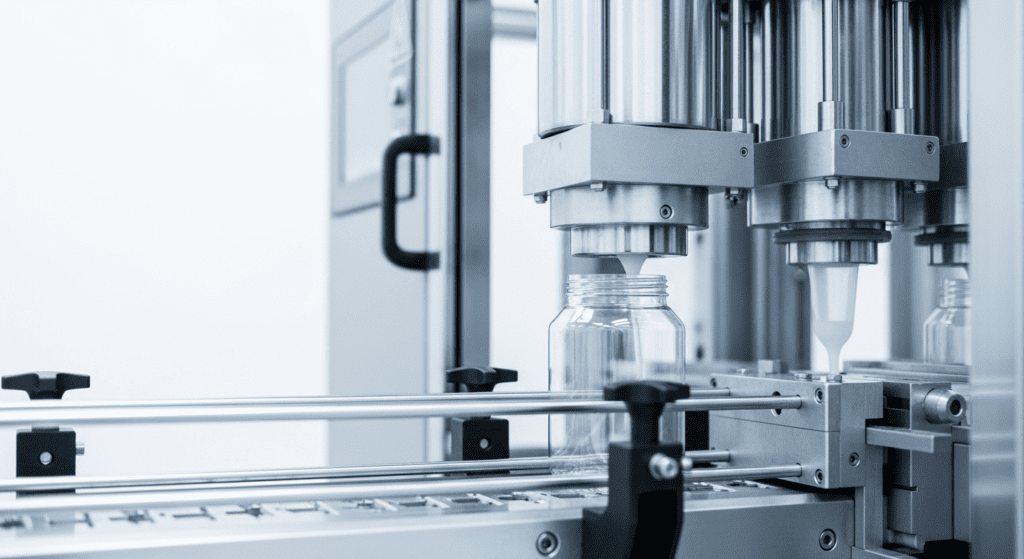

How Linear-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines Work
Linear machines use a conveyor system to move containers through each step. The plastic parison drops into molds at the first station.
The molds close and blow the containers into shape. A conveyor then moves these formed containers forward.
At the next station, filling happens while containers keep moving slowly. This allows for very precise fill volumes.
The containers continue to the sealing station on the same conveyor. After sealing, they might pass through cooling or inspection stations.
Some linear machines add extra steps like printing or labeling. The straight-line design makes it easy to add these special features.
Features of Linear-Type Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machines
- Modular design – Add or remove stations based on your needs
- Medium speed – Produces 5,000 to 20,000 units per hour
- In-line processing – Can add printing, inspection, or other steps easily
- Precise filling – Achieves fill accuracy within 0.5% of target volume
- Flexible layouts – Fits into existing production lines well
- Easy access – All stations are reachable for cleaning and maintenance
- Special applications – Great for products needing extra sterilization or mixing
- Scalable production – Start with basic setup and expand later
Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) Machine Types Comparison
| Feature | Rotary-Type BFS | Linear-Type BFS | Shuttle-Type BFS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Circular/rotational layout with stations arranged around a central axis | Straight-line configuration with sequential stations | Back-and-forth movement between stations |
| Production Speed | High (typically 6,000-20,000+ units/hour) | Medium to High (varies by line length) | Lower to Medium (due to shuttle movement) |
| Footprint | Compact circular footprint | Longer linear footprint | Moderate footprint |
| Flexibility | Limited – optimized for high-volume, single products | High – easy to reconfigure for different products | High – adaptable to various container sizes |
| Changeover Time | Longer due to multiple stations | Shorter – easier access to components | Medium – depends on shuttle configuration |
| Initial Investment | High | Medium to High | Lower to Medium |
| Maintenance Access | More complex – stations arranged in circle | Excellent – linear access to all stations | Good – accessible shuttle mechanisms |
| Product Suitability | Large volume, standardized containers | Various volumes, multiple product types | Small to medium batches, specialized applications |
| Container Size Range | Limited range optimized for specific sizes | Wide range of container sizes | Flexible container sizing |
| Sterility Assurance | Excellent – continuous enclosed process | Excellent – enclosed linear process | Good – depends on design implementation |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency at full capacity | Good overall efficiency | Variable – depends on shuttle frequency |
| Typical Applications | Pharmaceuticals, eye drops, large-scale production | Pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food products | R&D, pilot production, specialized containers |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale – requires new equipment | Easier to scale by adding stations | Limited scalability |
| Quality Control Integration | Integrated inspection at multiple stations | Easy integration along the line | Flexible inspection point placement |
| Operator Training | Complex – requires understanding of rotary mechanics | Moderate – straightforward linear process | Easier – simpler shuttle operations |


