Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS) machines work by forming plastic film into a vertical bag, filling it with product, then sealing it. The process starts with a roll of film shaped into a tube. The machine fills the bag with product, heat-seals it, and cuts it for final packaging.
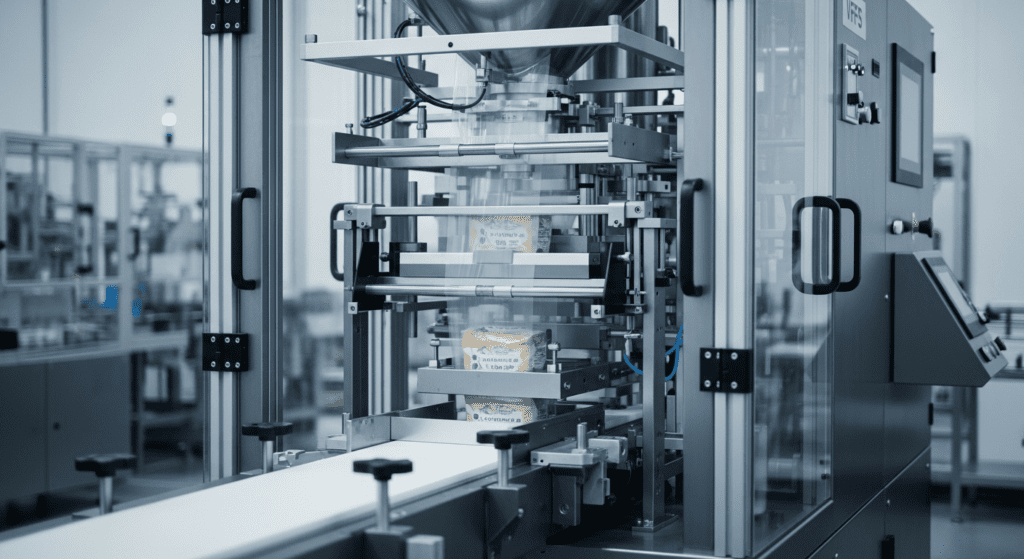

What is Vertical Form-Fill-Seal Packaging Machine
A Vertical Form-Fill-Seal packaging machine is an automated system that creates bags from a flat roll of film, fills them with product, and seals them shut in one continuous process. These machines work by pulling plastic film downward, forming it into a bag shape, dropping product inside, and sealing both ends.
How Vertical Form-Fill-Seal Packaging Machines Work
The VFFS process follows seven main steps that transform a flat sheet of film into a filled and sealed package.
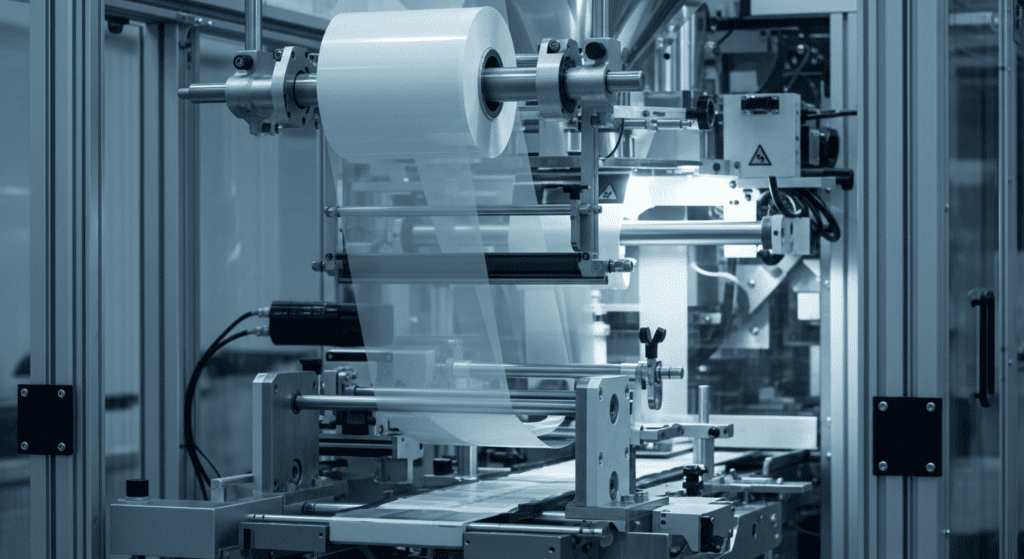
1. Film Unwinding and Transport
The process starts with a large roll of film (called rollstock) mounted on a shaft or spindle at the back of the machine.
As the machine runs, motor-driven belts or rollers pull the film downward toward the front. (On some machines the heated sealing jaws themselves grip and pull the film through.) This film transport system drags the web off the roll and into the machine.
Heavy-duty machines may also use a power-driven unwind (a motorized brake or roller) to help pay out large, heavy rolls smoothly.
2. Film Tensioning and Alignment
As the film unwinds, it passes over a weighted dancer arm (a pivoting roller arm) that moves up and down to maintain constant tension. This prevents slack or wrinkles.
The film web then goes under edge-guidance sensors and (if printed) a registration photo-eye. The photo-eye reads printed marks on the film to ensure any printing is aligned and timed correctly. Edge-tracking sensors detect if the film drifts sideways; if it does, a servo or cam will nudge the film carriage to recenter the web.
These tension- and tracking systems together keep the film straight and at the proper position so that each bag will be cut and sealed in the right place.
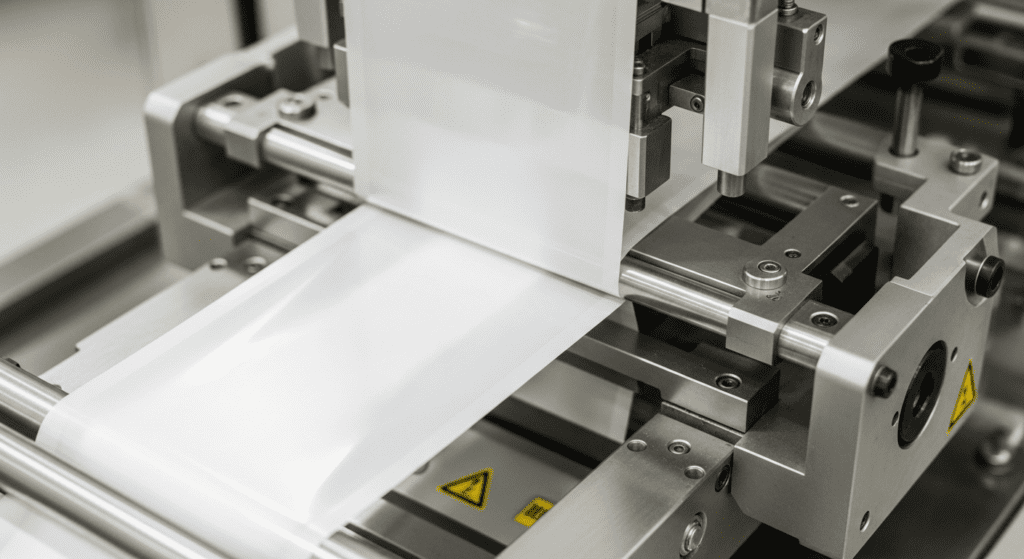
3. Bag Forming (Forming Collar and Tube)
The film is drawn over a cone-shaped forming collar and around a vertical metal forming tube at the front of the machine. This collar/tube combination shapes the flat film into a vertical cylinder – essentially forming the bag’s walls.
Two vertical pull-down belts (or vacuum belts) on either side of the forming tube grip the film and pull it downwards, controlling the bag length as it is formed.
When wrapped around the tube, the two vertical edges of the film overlap at the back. This overlap will later become the rear seam of the bag. Depending on the setup, the machine can make a lap seal (edges overlapped flat) or a fin seal (edges sealed along the inner sides, creating a fin-like seam). A lap seal is flatter and uses slightly less film, while a fin seal may be stronger.
A rotary encoder on the forming collar measures how much film has moved, allowing the control system to stop or meter film precisely to the programmed bag length.
4. Vertical Sealing
Once the film tube is formed to the correct length, a vertical sealing jaw closes on the back overlap of the tube, applying heat (or ultrasonic vibration) and pressure to fuse the film edges into a continuous seam. This creates the back seal of the bag.
In intermittent VFFS machines, the film stops moving while the vertical jaw heats the seam; in continuous-motion machines, a moving vertical bar can seal on-the-fly without stopping the film.
After this step, the film is essentially a long sealed tube open at the top.
5. Product Filling
With the bag formed and sealed on the back, product is dispensed into the open top of the tube via the forming tube. The machine synchronizes the fill so that the bag is held in place (or moving slowly) while it is filled.
Different products require different dosing systems. The dosing equipment measures each portion to the correct net weight or volume before dropping it down the tube. Once the correct amount is dispensed, the machine moves to the next step.
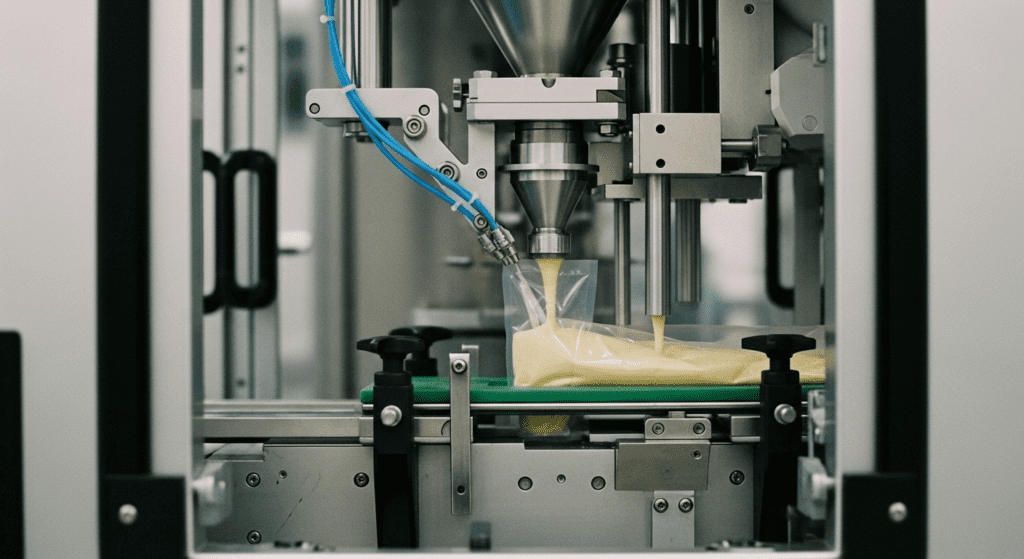

6. Horizontal Sealing and Cutting
Heated horizontal sealing jaws seal across the film to form bag ends and a built-in knife cuts the film to separate the bags. After filling, one or two heated horizontal jaws descend across the tube, clamping above the filled product. The jaws heat-seal the film, creating the top seal of the filled bag and simultaneously the bottom seal of the next bag below it.
In effect, they seal off one bag and start the next one in a single motion. A sharp blade integrated into the jaws then cuts through the film at this seal line. The result is that the filled bag is sealed shut at the top, and the remaining film continues downward to form the next bag.
7. Bag Discharge
Immediately after sealing, the cut bag is released. A reciprocating knife or blade (often integrated in the sealing jaws) has severed the bag from the continuous web. The jaws open and the finished pouch drops out of the machine.
The discharged bag typically falls onto a conveyor or into a collection bin. From here, the finished bags can go to downstream equipment (such as weigh-checkers, labelers, or case packers) for final processing. The machine then repeats the entire cycle for the next bag.
Learn more about How Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS) Packaging Machines Work
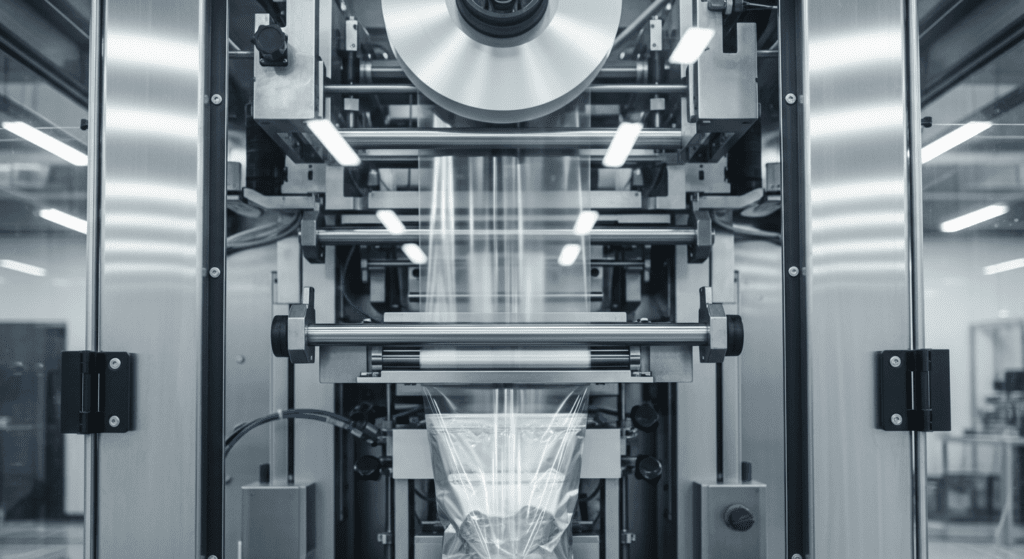
Types of Vertical Form-Fill-Seal Packaging Machines
VFFS machines come in different configurations to match various production needs and product types.
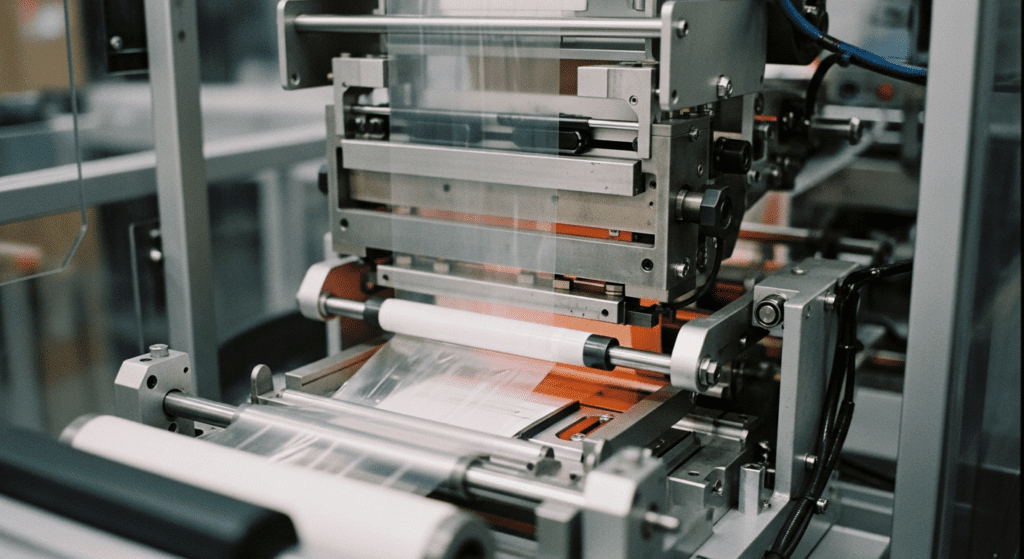

Intermittent VFFS
Intermittent VFFS machines stop the film movement during sealing and cutting operations. The film advances, stops for sealing, then advances again in a start-stop motion.
These machines work best for products that need longer sealing times or precise fill weights. They typically run at speeds of 30 to 120 bags per minute.
The start-stop action allows for better control over seal quality. It also makes these machines ideal for handling difficult films or creating complex bag styles.
Continuous VFFS
Continuous motion machines never stop the film flow. The sealing jaws move with the film during sealing, then return to starting position.
This design allows much higher speeds, often reaching 200 to 300 bags per minute. The constant motion reduces wear on mechanical parts and film.
Continuous machines excel at high-volume production of simple bag styles. They’re perfect for snack foods, candy, and other products that need fast packaging.
Modern VFFS
Today’s VFFS machines incorporate advanced technology for better performance and flexibility:
- Servo-driven (electric motors) provide precise control over every moving part. They adjust speed instantly and remember multiple product settings.
- Pneumatic (air cylinders) power the sealing jaws and cutting mechanisms on many machines. They deliver consistent pressure and fast cycling times.
- Dual-web VFFS machines run two film rolls simultaneously. This doubles production capacity without doubling floor space.
Learn more about Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS) Machine Troubleshooting Guide
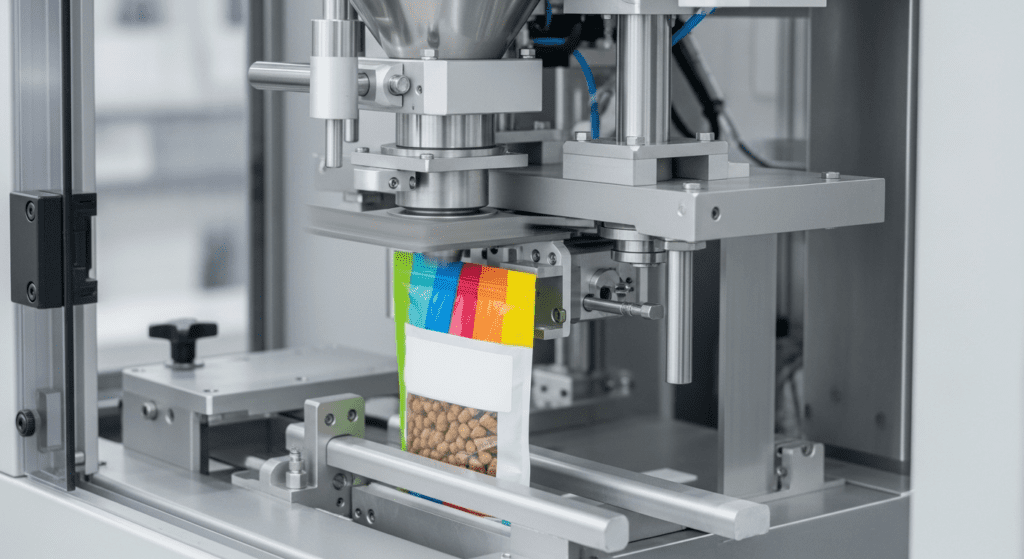
Components of Vertical Form-Fill-Seal Packaging Machines
Understanding the main components helps operators maintain their machines and troubleshoot problems:
- Film Delivery System includes the unwind stand, dancer rollers, and web guides that control film movement
- Forming Collar and Tube shape the flat film into a bag and guide product into the package
- Vertical Sealing Jaws create the back seal that runs the length of the bag
- Horizontal Sealing Jaws form the top and bottom seals while incorporating the cutting mechanism
- Cutting Mechanism separates individual bags using straight or serrated blades
- Filling System measures and dispenses the correct amount of product into each bag
- Sensors and Controls monitor every aspect of operation from film position to seal temperature
- Auxiliary Modules add features like gas flushing, date coding, or hole punching
Common Packaging Materials
VFFS machines work with many different films, each chosen for specific product needs:
- Polyethylene (PE) offers good moisture barrier and heat sealing properties for bread and frozen foods
- Polypropylene (PP) provides clarity and stiffness for snack foods and candy
- Laminated films combine multiple materials for enhanced barrier properties and graphics
- Metalized films add oxygen barrier and visual appeal for coffee and snacks
- Paper laminates give an eco-friendly option for dry goods and powders
- Biodegradable films meet sustainability goals while maintaining product protection

VFFS vs HFFS
Vertical Form-Fill-Seal and Horizontal Form-Fill-Seal machines serve different packaging needs. VFFS machines form packages vertically with product flowing down through the machine, while HFFS machines create packages horizontally with products placed from the side.
| Aspect | VFFS | HFFS |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Vertical operation – film travels downward | Horizontal operation – film travels horizontally |
| Product Flow | Products drop vertically by gravity | Products are pushed/placed horizontally |
| Package Types | Pillow bags, gusseted bags, stick packs | Pouches, sachets, four-side seal bags |
| Best For | Free-flowing products (chips, nuts, powders, liquids) | Solid items (cookies, bars, medical devices) |
| Footprint | Smaller floor space, taller height | Larger floor space, lower height |
| Speed | Generally faster (up to 120+ bags/min) | Moderate speed (30-100 packages/min) |
| Film Usage | More efficient film usage | Can use pre-printed film more easily |
| Product Handling | Gravity-assisted, minimal product damage | Better for fragile/delicate items |
| Seal Types | Back seal, lap seal | Three-side seal, four-side seal |
| Typical Industries | Snack foods, coffee, frozen foods | Pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, hardware |
| Cost | Generally lower initial investment | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Simpler design, easier maintenance | More complex, higher maintenance |
| Changeover Time | Faster format changes | Longer changeover times |
| Integration | Easy to integrate with weighers/fillers | Better for inline production with other equipment |



